Value is enshrined in the effort of others. Sometimes this is captured or represented in a thing, but the value is not the thing in itself.
It’s the time, creativity, and effort invested into the thing that imbue it with worth. This principle extends beyond mere objects to experiences, relationships, ideas and computing services. The value we assign to these aspects of life is reflective of the human energy, emotion and intelligence they represent.

Figure 1: The image conveys the idea that in the digital age, the value is placed more on the digital content (files) than on the physical devices (things) themselves.
It is surprising therefore to note that computing services that replace services where there was previously a human in the loop are thought of as an equivalent that can command the same fee, or even any fee.
When the supermarket checkout machine says “Thank you” to me as I pay, I tell it to f**k off. A little piece of human rage muttered to a machine that cannot care.
We will replace all the services that we can. That is certain. Going to the doctor, employing a designer, reporting a car crash to the police, doing social research, answering email, buying insurance, visiting the bank, education. Our whole environment is changing. There is less human to human interaction.
This kind of value shift has happened before. In the 1880s craft produced goods were replaced by mass produced goods with no soul. The Luddites of 1810 and the Arts and Crafts movement of the 1880’s and are only quaint protest movements against mechanisation that progress rolled over. The conflict and the sentiments are nicely captured by Robert Calvert in his 1980 song Ned Ludd:
They said Ned Ludd was an idiot boy
That all he could do was wreck and destroy, and
He turned to his workmates and said: Death to Machines
They tread on our future and they stamp on our dreams.
In the past, the human element – the expertise, personal touch, and judgment – was a significant part of the value proposition. However, now and forever into the future with so many computational services, the efficiency, consistency, and scalability offered is preferred and valued. The transition from human-driven to computer-driven services signifies a redefinition of value.
This trend raises questions about the future of work and the valuation of human skills versus automated systems. It also challenges us to consider what aspects of human input are irreplaceable by technology and how we should appropriately value such contributions.
The change catalysed by computational services will yield up replacement and mutant solutions as well as giving rise to entirely novel concepts not previously imaginable.
Computational Services are faster, cheaper and efficient. They are also different. Whole value ecosystems are on the move. Here are five areas undergoing massive change.
- Monitored Security
- Customer Support and Services
- Automated grading in Education
- Translation Services
- Banking
1. Monitored Security:
A premises is protected by CCTV cameras. Motion detection cameras detect the presence of an intruder and send an alert event to a central monitoring station where a human operator reviews the video and takes appropriate escalating action. This service commands a substantial monthly fee.
Monitored security can be replaced by a self-monitored system which automatically on foot of the trigger event sends a message to property owners. This do-it-yourself service has reduced value and can struggle even to command a modest monthly subscription fee.
In the traditional model, the presence of a human operator in a central monitoring station adds significant value. This person not only reviews alerts but also exercises judgment, potentially recognizing false alarms or identifying subtleties that a machine might miss. Their expertise and decision-making capabilities in escalating situations are integral to the service’s value.
However, when this service is replaced by an automated system that merely sends alerts to property owners, all those elements are lost.
Should a security breach occur self-monitoring property owners need to escalate by calling law enforcement but without the contact base and authority of trained staff in a Central Monitoring Station. Good luck with that!
Even though there are problems with self-monitored security, and it does not suit everybody, irrevocable change in the marketplace is underway. Monitoring centres are offering half service and hybrid solutions to try and compete. But it is very hard to compete with a cost-free service.
2. Customer Support and Service:
Traditionally, customer support involved direct interaction with a human representative. This representative could empathize with the customer, understand nuanced problems, and provide personalized solutions. Human interactions in customer service often involve a level of personal care and understanding that can lead to a more satisfying customer experience.
With automated customer service technologies, such as chatbots and AI-driven support systems, this human element is eliminated. While these systems offer 24/7 availability and immediate responses, they lack the ability to fully understand complex or unique customer issues. For many customers, talking to a machine can be frustrating, especially if their problem is not addressed effectively.
This shift towards automated customer support can lead to a perception of decreased value in the service, as customers miss the personal touch and nuanced understanding that human representatives provide. Consequently, even though these computational services might be more efficient in terms of cost and time, they struggle to achieve the same level of customer satisfaction and loyalty that is often fostered through human interactions.
Press 9 to ‘yell at the moon’.
3. Automated Grading in Education:
Traditional educational assessment involves teachers or professors personally grading student work. This process allows educators to evaluate answers for correctness and understand a student’s thought process, reasoning, and creativity. Teachers can provide personalized feedback, recognizing the unique strengths of each student.
With the introduction of automated grading systems, which use algorithms to assess student work, this nuanced and personalized aspect of grading is lost. While such systems can efficiently handle large volumes of work and provide quick feedback, they lack the ability to accurately judge more subjective aspects of student work, such as the quality of argumentation, the originality of ideas, or the clarity of expression.
As a result, the use of automated grading systems can lead to a perception of a less valuable educational experience. Students might feel that their work is not being truly ‘seen’ or understood, and the lack of personalized feedback can impact their learning and development.
More than this, why go to school at all, sure no-one is going to look at your script. Stay at home and learn stuff by yourself on YouTube instead! Is going to a School or University building still a thing?
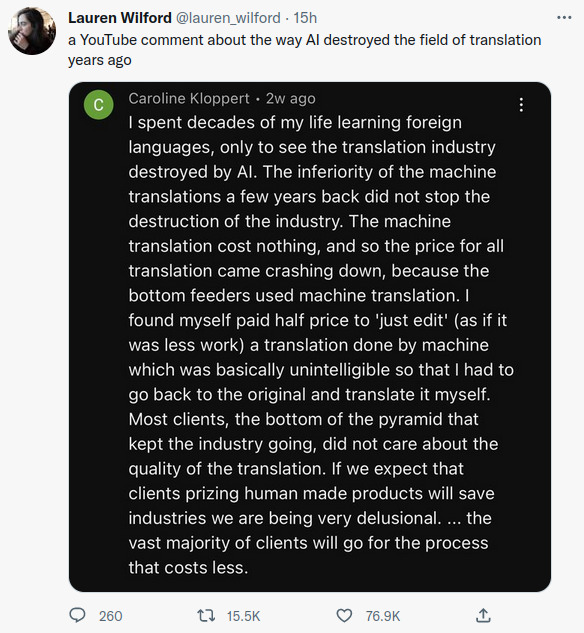
4. Translation Services:
Traditionally, translation has been a highly skilled profession. Good human translators understand the context, tone, and subtleties that are essential for accurate and culturally sensitive translations.
With the advent of automated translation services like Google Translate, the process of translation has become instantly accessible and highly efficient. These services can quickly translate large volumes of text and are continuously improving in accuracy due to advances in machine learning and natural language processing. However, despite these advancements, automated translations often fall short in accurately conveying the full meaning, especially with complex, nuanced, or context-heavy content. They may struggle with idiomatic expressions, cultural nuances, and professional or technical jargon.
As a result, automated translation services are often perceived as less valuable for tasks requiring a high level of accuracy, cultural sensitivity, and contextual understanding. This limitation is particularly evident in professional settings, such as legal, medical, or literary translations, where the nuances and exactness of language are paramount. The gap in quality between human and machine translations in these scenarios highlights the irreplaceable value of human expertise in certain domains.
The Pope for instance would probably not use a computational system to translate his messages. Those messages need to be translated very carefully to ensure that every nuance of meaning is correctly annunciated.
The idea however that being a translator is a viable professional career is now non-existent. That boat has sailed!
5. Banking:
Revolut is a neobank. A neobank is a bank that operates exclusively using online banking without traditional physical branch networks.
Revolut, founded in 2015, started as an app-based banking alternative with a multi-currency card. Revolut’s focus has been to offer everything opposite to traditional banks. This includes allowing users to spend globally at real exchange rates, eliminating unfair fees for standard transactions, and providing services like countless payments and ATM withdrawals. With more than 250 thousand daily active users, it’s clear that Revolut’s mission to provide better alternatives to traditional banks is resonating with consumers.
Beyond financial services, Revolut aims to surpass traditional banks by offering real-time spending alerts, budgeting controls, bill splitting, and the ability to immediately freeze cards. Additionally, it provides overseas medical insurance and 24/7 customer support.
Revolut seeks to explore new opportunities in the banking and fintech industry. This includes services like ‘Vaults’ for saving money and offering investment opportunities in cryptocurrencies like ‘Bitcoin Cash’.
In a move to disrupt traditional banking systems further, Revolut is building a commission-free trading platform within its app. This feature will enable users to invest in stocks and exchange-traded funds.
In summary, Revolut’s innovative, customer-centric approach, coupled with its technological advancements and diverse service offerings, is redefining the traditional banking model. By offering greater convenience, transparency, and a wide range of financial services, Revolut is not just an alternative to traditional banking but a significant force in transforming how banking is perceived and conducted in the digital age.
So, if you are trying to open a bank account for a new business. Why go to the trouble? Just open up a new Revolut account instead!
Conclusion
So, what is this essay about? It is only a recognition that whole systems are becoming automated and there is no longer a human in the loop. The system is often now just an automated response. This devalues a system, any system, to a considerable extent. This is because things/systems/robots are not valued, people are.
We have entered a time where we rely on automated and AI services. Some people are excited, some are fearful of this. But there is no choice, all that is discussed here are the consequences of automation. One clear consequence is that perceptions of value are changing. In some cases, the new Automated AI Service reduces the value of the activity to near zero. Translation services for example. In some other cases the automated service is not an equivalent of the person-to-person service it is an entirely different concept. Revolute for example is changing the idea of banking.
The prospect that someday soon we will all have a personal robot agent that will call the airline to get your money back from a cancelled flight automatically making the right menu selections and never giving up seems like a very attractive high value proposition. We will dispatch a robot agent to meet the agents that we meet.
Perhaps, at least in some contexts, we might prefer robots.
08/12/23 Roman set by: Anthony Hutton. Italics by: ChatGPT4